Key Takeaways:
- The basics of neurons
- Neuronal structure explained
- Types and functions of neurons
- How neurons communicate
- Impact on mental health
Introduction to Neurons
Neurons are the fundamental building blocks of our nervous system. They play a crucial role in everything from our thoughts and feelings to our movements and sensations. Understanding neurons is essential for grasping how our brains function and how we experience the world.
Each neuron in the human brain is a specialized cell designed to transmit information to other nerve cells, muscle, or gland cells. Neurons use electrical impulses and chemical signals to communicate, creating the complex web of interactions that underpins our mental and physical activities.
In my experience, comprehending the basic functions of neurons can greatly enhance one's appreciation of the intricate processes that govern our behavior and mental health. By diving deeper into the world of neurons, we can better understand how our brain works, and this knowledge can be empowering.
The Basic Structure of a Neuron
A neuron typically consists of three main parts: the cell body (or soma), dendrites, and an axon. The cell body contains the nucleus, which houses the neuron's genetic material and is responsible for maintaining the cell's health and functionality.
Dendrites are tree-like structures that extend from the cell body. They receive signals from other neurons and convey this information to the cell body. The axon, a long, slender projection, transmits electrical impulses away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
This basic structure enables neurons to efficiently process and transmit information. As neuroscientist Eric Kandel notes in his book, "In Search of Memory," the structure of neurons is a marvel of biological engineering, allowing for the rapid and precise transmission of signals across vast networks within the brain.
Understanding these structural components is fundamental to grasping how neurons function and interact with each other. By exploring the anatomy of neurons, we gain insights into the remarkable capabilities of the human brain.
Types of Neurons and Their Functions
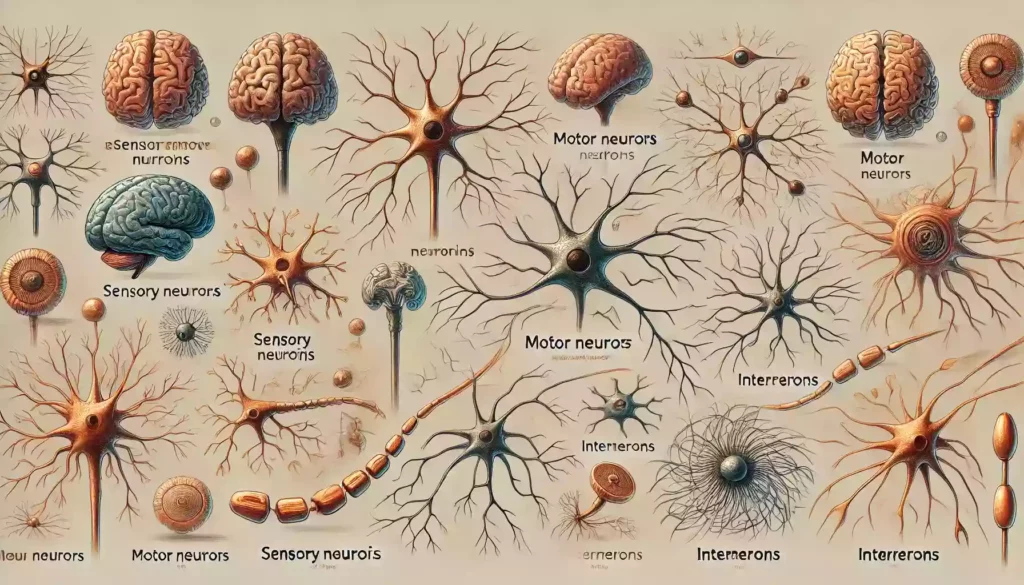
Neurons come in various shapes and sizes, each tailored to perform specific functions within the nervous system. Understanding these types is crucial to appreciate the diverse roles they play in our body.
Sensory neurons, for instance, are responsible for converting external stimuli from the environment into internal electrical impulses. These neurons allow us to perceive the world through our senses.
Motor neurons, on the other hand, transmit signals from the brain and spinal cord to muscles, enabling movement. Without motor neurons, voluntary actions such as walking or speaking would be impossible.
Then there are interneurons, which act as connectors between sensory and motor neurons. They are found primarily in the brain and spinal cord and are integral to reflexes and higher functions such as learning and decision-making.
Each type of neuron has a unique structure that suits its specific function, making the nervous system an incredibly efficient network. The diversity of neurons is a testament to the complexity and adaptability of our brains.
How Neurons Communicate: Synapses and Neurotransmitters
Communication between neurons occurs at specialized junctions called synapses. A synapse consists of a presynaptic ending that contains neurotransmitters, a synaptic cleft, and a postsynaptic ending that receives the neurotransmitters.
When an electrical signal reaches the end of a neuron, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These chemical messengers then bind to receptors on the adjacent neuron, propagating the signal. This process is known as synaptic transmission.
Neurotransmitters are vital to this process and include chemicals such as dopamine, serotonin, and acetylcholine. Each neurotransmitter has a specific role, influencing everything from mood and arousal to muscle movement and cognition.
As neuroscientist Candace Pert elaborates in "Molecules of Emotion," neurotransmitters are the key to understanding how our brains regulate emotions and behaviors. The balance and function of these chemicals are crucial for maintaining mental health and well-being.
By studying synaptic transmission, we gain insights into how our brains process information and respond to various stimuli. This knowledge is essential for developing treatments for neurological disorders and improving mental health.
The Role of Neurons in the Brain

Neurons are the workhorses of the brain, responsible for its many functions. They form complex networks that allow us to think, feel, and move. These networks enable everything from basic survival functions to advanced cognitive processes.
In the cerebral cortex, for example, neurons are involved in higher-order brain functions like perception, thought, and decision-making. Neurons in the hippocampus are crucial for forming and retrieving memories. In the limbic system, neurons regulate emotions and behavioral responses.
The brain's ability to process vast amounts of information and respond appropriately is due to the specialized functions of neurons in different regions. Each area of the brain has a distinct role, and neurons ensure these regions work together seamlessly.
Neuroplasticity: How Neurons Adapt and Change
Neuroplasticity is the brain's remarkable ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. This adaptability is essential for learning, memory, and recovery from brain injuries.
When we learn something new, our brain cells (neurons) form new connections, strengthening the pathways used. This process explains why practice and repetition are critical for mastering new skills. According to Dr. Norman Doidge, author of "The Brain That Changes Itself," neuroplasticity is a fundamental property of the brain, allowing it to change its structure and function in response to experience.
Neuroplasticity also plays a significant role in recovery after brain injuries. When neurons are damaged, the brain can sometimes rewire itself to compensate for lost functions. This ability offers hope for rehabilitation therapies aimed at helping individuals regain abilities after strokes or traumatic brain injuries.
Understanding neuroplasticity highlights the brain's resilience and potential for growth. By engaging in activities that challenge our minds, we can harness this power to improve cognitive functions and adapt to new circumstances.
Neurons and Mental Health
The health of our neurons is directly linked to our mental well-being. Various mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia, are associated with disruptions in neuronal function and communication. For instance, imbalances in neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine can lead to mood disorders.
Research has shown that chronic stress can damage neurons, particularly in areas of the brain involved in memory and emotion, such as the hippocampus and amygdala. This neuronal damage can contribute to the development of mental health issues. Understanding these mechanisms allows for better-targeted treatments and therapies.
As psychiatrist Dr. Daniel Amen explains in his book "Change Your Brain, Change Your Life," improving neuronal health through lifestyle changes, such as diet, exercise, and mindfulness, can have a profound impact on mental health. Neuroplasticity also plays a role here, as engaging in positive activities can help rewire the brain and improve mental resilience.
Addressing mental health involves a holistic approach that considers the state of our neurons. By fostering healthy neuronal function, we can enhance our overall mental well-being and resilience.
Neurons and Human Behavior
Our behaviors, from simple reflexes to complex decision-making, are governed by neuronal activity. Neurons process information, generate responses, and adapt based on experiences, shaping how we interact with the world.
The prefrontal cortex, a brain region rich in neurons, is crucial for decision-making, social interactions, and self-control. Neurons in this area help us plan, focus attention, and inhibit inappropriate behaviors. Damage to the prefrontal cortex can result in impulsivity and difficulty with complex tasks.
Furthermore, the mirror neuron system allows us to understand and imitate the actions and emotions of others. This system, discovered by neuroscientist Giacomo Rizzolatti, plays a significant role in empathy and social learning. Mirror neurons enable us to connect with others on a deep level, influencing our social behaviors and interactions.
Understanding the neuronal basis of behavior helps us appreciate the complexity of human actions. By studying neurons and their networks, we can develop strategies to enhance positive behaviors and address behavioral issues.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Neurons
Understanding neurons is fundamental to comprehending how our brain functions and, by extension, how we experience life. Neurons are at the heart of every thought, emotion, and action. They shape our memories, influence our behaviors, and are central to our mental health.
The intricate networks of neurons in our brain are responsible for the incredible capabilities of human cognition. By studying neurons, we gain insights into everything from basic reflexes to complex decision-making processes. This knowledge is not only fascinating but also immensely practical. It allows us to develop better treatments for neurological and mental health disorders, improve educational strategies, and enhance overall brain health.
As we continue to explore the world of neurons, we uncover more about the human condition. The brain's adaptability and resilience, showcased through neuroplasticity, highlight the potential for growth and recovery. By taking care of our neurons through healthy lifestyle choices, we can enhance our mental and emotional well-being.
In essence, neurons are the key to unlocking the mysteries of the mind. By deepening our understanding of these remarkable cells, we empower ourselves to lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Recommended Resources
- Dr. Norman Doidge, "The Brain That Changes Itself"
- Dr. Daniel Amen, "Change Your Brain, Change Your Life"
- Candace Pert, "Molecules of Emotion"




Recommended Comments
There are no comments to display.
Create an account or sign in to comment
You need to be a member in order to leave a comment
Create an account
Sign up for a new account in our community. It's easy!
Register a new accountSign in
Already have an account? Sign in here.
Sign In Now